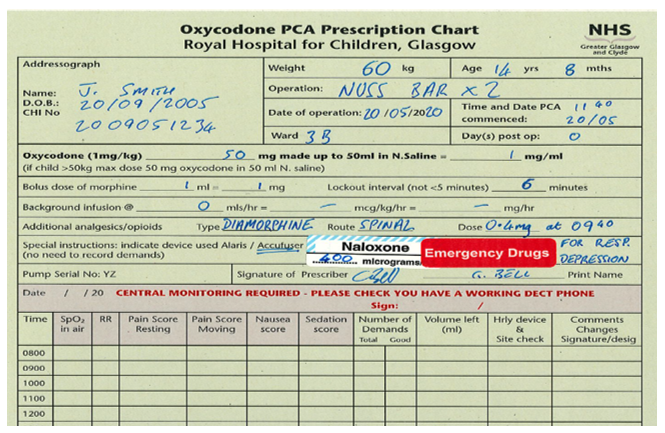
As per the WHO ladder, paracetamol is the first line non-opioid analgesic of choice in RHC. It can be given IV (usually only in theatre, in patients who are NBM or not tolerating oral diet, and in other specific circumstances), or Oral/Rectal. Dosing varies by age and by route chosen, as shown in the table below.
Guidelines can also be found in the BNFc by following this link BNF for Children
Disclaimer: For drug dosing in the context of infants in NICU, please refer to the Perinatal Network Monograph linked here: Local / Regional Drug Monographs - Scottish Perinatal Network
Despite BNFc using age banded dosing we would always advocate using weight banded dose calculations wherever possible. Age banded dosing typically under doses at higher ages, and over doses at lower ages. This is particularly true for the extremes of weight within each age category.
Both double dosing and overdosing of paracetamol in paeds (particularly 10x dosing error) is a significant risk in paediatric practice. Please consider a two person check of prescription and/or administration, particularly in the infant population. A good rule of thumb is a RULE OF 10:
- 10mg/kg dose
- under 10kg
- 10ml syringe (or smaller)
This is a good rule of thumb for rotating trainees and a simple calculation which can be used to minimise errors and improve safety.
Obese children present a challenge when calculating their optimal therapeutic paracetamol dose. Most paediatric centres now use Adjusted Body Weight (AdjBW) to calculate paracetamol. If you think the child you are looking after is overweight for their age, please dose adjust. There are many apps which allow accurate calculation of AdjBW, such as Paeds Prescribing Pro.
Caution should also be exercised in children with liver dysfunction and in neonatal unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia. In these children we advise reducing the loading dose and increasing the dosing interval of paracetamol. In practical terms this would be 10mg/kg dosing, 8 hourly interval with a 30mg/kg/day limit, as for ‘term neonates’- see table above. Prescribing in children with haem oncological diagnoses should also be done with caution, and in consultation with the parent team. In these children, paracetamol may mask the fever which can accompany neutropenic sepsis.