5.1.1 Blood Group:
Haemopoietic Stem Cell Transplant (HSCT) Patients
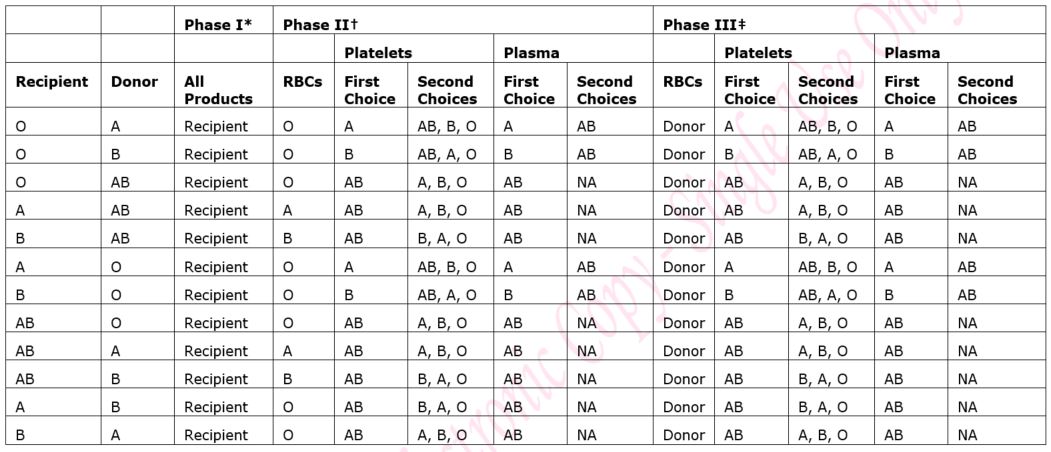
Recipients of haemopoietic stem cell transplants may be of a different blood group to their donor and this can lead to an ABO major or minor mismatch. The patient’s transplant schedule will clearly state the blood group(s) of red cells, platelets and Octaplas (fresh frozen plasma) that should be transfused. The transplant schedule should always be checked and the instructions followed. See also section 5.4 below.
Haemoglobinopathy and Bone Marrow Failure Syndrome Patients
These patients may be regularly transfused throughout life and, because of this, are extensively red cell phenotyped to minimise the risk of allo-immunisation. Their red cell phenotype should be documented in their casenotes. The Blood Bank will require advanced warning to provide appropriate blood.
5.1.2 Irradiated Blood and Blood Products:
Please see the GG&C Blood Transfusion Special Requirements Guideline for further information and the notification form [Staffnet link], which must be completed for every patient with special transfusion requirements.
All blood is now leucodepleted by the Scottish National Blood Transfusion Service (SNBTS) immediately after donation to prevent the transmission of variant CJD. However, even the very small number of white cells that remain after leucodepletion can engraft in severely immunocompromised recipients and cause Transfusion Associated Graft Versus Host Disease (TA-GVHD), which is usually fatal.
In normal immunocompetent recipients these white cells are cleared by the immune system and cause no clinical problems.
Irradiation of blood and blood products prevents the proliferation of transfused white cells in the recipient and is completely effective in preventing TA-GVHD. Irradiated blood must also be available for the donor during the stem cell collection procedure, in the unlikely event that this is required.
Table 1 below lists the patient categories that require irradiated blood products and these include:
- All transplant patients (allogeneic and autologous), all patients receiving purine analogues (including fludarabine and clofarabine) containing regimens, all patients with Hodgkin’s disease, all patients with or suspected of having congenital immunodeficiency and all patients with Di George syndrome or those undergoing cardiac surgery who may have Di George syndrome
- All platelet and granulocyte transfusions are routinely irradiated by the SNBTS.
- All cellular blood products donated by relatives
- All patients with congenital immunodeficiencies
- Blood components that do NOT require irradiation: fresh frozen plasma (Octaplas), cryoprecipitate or fractionated plasma (BSH Guidelines, 2020).
Table 1: Duration of provision of irradiated products
|
|
START IRRADIATED PRODUCTS
|
STOP IRRADIATED PRODUCTS
|
|
All types of HSCT
|
2 weeks prior to HSCT and throughout conditioning
|
According to type of transplant – see below
|
|
Allogeneic HSCT
|
2 weeks prior to HSCT and throughout conditioning
|
Lifelong*
|
|
Autologous HSCT
|
From mobilisation chemotherapy or 14 days before the stem cell collection (whichever is earlier)
|
3 months post SCT if no TBI
6 months post SCT if TBI
|
|
HSCT for SCID
|
2 weeks prior to HSCT and throughout conditioning
|
Lifelong
|
|
Collection of autologous or allogeneic BM or PBSC
|
From mobilization or two weeks before (and during) the collection
|
Following completion of collection
|
|
Patients treated with purine analogues (even if no HSCT)
|
From start of chemotherapy cycle containing the purine analogue
|
Lifelong
|
|
Patients with aplastic anaemia undergoing treatment with ATG or Alemtuzumab
|
From start of treatment
|
Following discontinuation of ciclosporin
|
|
Patients undergoing PB lymphocyte collections for future CAR-T cell re-infusion
|
7 days prior to collection and during procedure
|
3 months following CAR-T cell infusion (unless conditioning, disease or previous treatment determine indefinite duration)
|
* Immune reconstitution may be greatly delayed following allogeneic HSCT and it is difficult to be sure when it has taken place, particularly if HSCT is from an unrelated or haplo-identical donor, and therefore cellular blood products are usually irradiated life-long after allo-HSCT.
5.1.3 CMV Negative Blood and Blood Products:
Leucodepletion significantly reduces the risk of transfusion related CMV transmission and therefore the majority of HSCT patients do not need CMV screened blood products. Appendix 1 lists the current recommendations for the transfusion of CMV negative and irradiated blood and blood products in the GG&C Special requirements guideline.
5.1.4 Hepatitis E (HEV) Seronegative Components:
In 2017 SNBTS commenced universal screening of blood products as HEV, as transmission of HEV can occur from blood transfusion, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. All platelet components and red cell components are now HEV negative. Frozen components (Octaplas (fresh frozen plasma) and cryoprecipitate) have a longer shelf life, though SNBTS indicate that all products requested are now HEV negative. As a consequence of this change the list of requirements for HEV selected components is less relevant, though is included in Appendix 1.