Glasgow Emergency Paediatric ECG Guideline (GEPEG)
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Objectives
This guidance document is to support RHC ED staff in utilisation of the ECG electronic reporting capacity and subsequent manual interpretation of the ECG.
This document also describes the patient disposition pathway options for children where an ECG has been performed.
Name, date of birth and CHI MUST be entered on ECG machine to gain appropriate paediatric ECG analysis for electronic report.
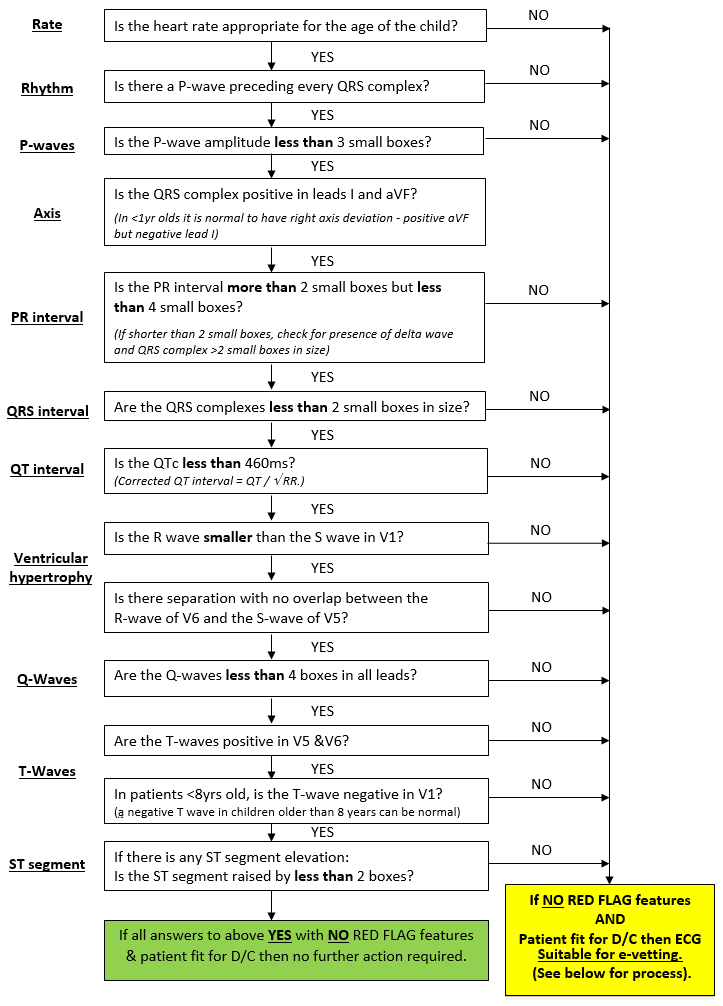
Once the ECG has been performed, the ECG machine provides an electronic report at the top of ECG. A quick manual checklist should be performed by the ED physician. (See below).
|
ECG RED FLAGS Syncope
Prolonged QTc
Patients presenting with ANY of the above ‘RED FLAGS’ MUST have an ECG and their case discussed with cardiology PRIOR to discharge even if ECG appears normal (includes out of hours). Consideration will be given to whether a 24 hour ECG / Holter monitor or exercise tolerance test will be required – on discussion with Cardiology team. |
‘Normal’ electronic report
If the electronic report is normal and the manual checklist is acceptable, no cardiology follow-up is necessary
‘Abnormal’ electronic report
If the electronic report is abnormal, manual checklist should be applied and detailed analysis of abnormality should take place. If the ED physician is confident, that on manually checking, the ECG is normal, no cardiology follow-up is required
Abnormality identified on manual checklist
If any abnormalities are identified on the manual checklist, then the ECG should be uploaded to clinical portal and ED discharge summary sent for e-vetting.
If in doubt upload ECG to clinical portal, send discharge summary for e-vetting, or if significant concerns, discuss with on call cardiology registrar.
If patient fulfils above criteria for e-vetting then ED staff to complete the ‘pink’ ED referral letter circling Cardiology and write “for e-vetting” next to this.
Please ensure the manual interpretation findings of the ECG are documented within the ED clinical notes with the indication for e-vetting noted.
This should go to the ED reception with the ED notes that will be scanned with a copy of the ECG and the onward referral to cardiology will be made by the ED secretaries via medical records.
The scanned ED card and ECG will be ‘e-vetted’ by the cardiology team when they receive the referral made by the ED secretaries as per the above referral process.
|
ELECTRODE |
PLACEMENT |
|
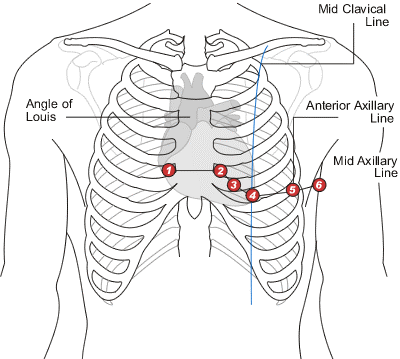
V1 |
4th Intercostal space to the right of the sternum |
|
V2 |
4th Intercostal space to the left of the sternum |
|
V3 |
Midway between V2 and V4 |
|
V4 |
5th Intercostal space at the midclavicular line |
|
V5 |
Anterior axillary line at the same level as V4 |
|
V6 |
Midaxillary line at the same level as V4 and V5 |
|
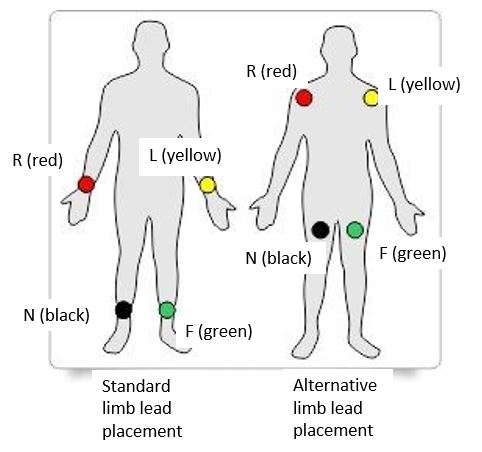
N (black) |
Above right ankle. (or upper leg, close to torso) |
|
R (red) |
Right forearm or right deltoid area |
|
L (yellow) |
Left forearm or right deltoid area |
|
F (green) |
Above left ankle. (or upper leg, close to torso) |
Last reviewed: 25 November 2020
Next review: 31 October 2025
Author(s): Dr Steve Foster – Consultant in Paediatric Emergency Medicine; Dr Karen McLeod – Consultant in paediatric Cardiology; Dr Jamie Wood – Trainee in Paediatric Medicine.
Approved By: Paediatric Emergency Department

