Audience
***ONLY FOR USE BY CLINICIANS COMPETENT IN IV KETAMINE SEDATION***
The use of IV Ketamine for Paediatric Procedural Sedation within RHC ED is at the discretion of the ED consultant and ED nurse co-ordinator. Appropriate case selection and clinical demands of the rest of the department may influence the availability of this service.
This SOP for IV Ketamine use in Procedural sedation can be adapted for use out with the Emergency Department however Minimum staffing , monitoring & equipment instructions should be replicated in the location the procedural sedation is being performed.
Only CLINICIANS COMPETENT IN IV KETAMINE FOR SEDATION may prescribe and administer IV ketamine for emergency procedural sedation.
During the COVID period the use of PPE for procedural sedation should follow the most up to date guidance released by Health Protection Scotland (HPS) with specific attention made to management for suspected/proven COVID positive versus non-COVID patients.
Warning – interventions required to manage adverse reactions may result in aerosol generation procedures (ie – suctioning or positive pressure ventilation). PPE appropriate for these interventions should be used.
Indications for use
- The decision to use IV ketamine sedation is that of the emergency department consultant and nurse in charge.
- Children aged 12 months and over
- Short painful procedure (ideally less than 20 minutes duration) e.g. fracture reduction / wound repair.
STRICT contraindications
- Procedures that will stimulate the posterior pharynx / intraoral procedures.
- Glaucoma or acute globe injury
Use Ketamine sedation with added caution in these situations:
- Children aged 12-24 months
- Airway assessment concerns identified (see airway assessment section below for details).
- Food within 2 hours
- Cardiovascular disease
- Poorly controlled seizure disorder
- Psychosis, porphyria
- Thyroid disease
- CNS or neuromuscular disorders
- Head injury with LOC, altered consciousness or vomiting
- Respiratory tract infection or lung disease
- Children with complex medical conditions
- History of previous airway surgery or congenital abnormality
Airway Assessment
Modified ‘LEMON’ assessment: any issues that may contribute to a difficult intubation?
L: Look for facial abnormalities / dysmorphism.
E: Evaluation of mouth opening, tongue size, oral cavity, tonsil size, jaw position (retrognathia)
M: Mallampati score if applicable (see below – if Class 3 or 4 then inform ED Consultant in charge)
O: Obstruction - any signs of upper airway obstruction, stridor, drooling, difficulty with secretions.
N: Neck - assess neck mobility (check for limited extension / disproportionally short neck).
Mallampati score:
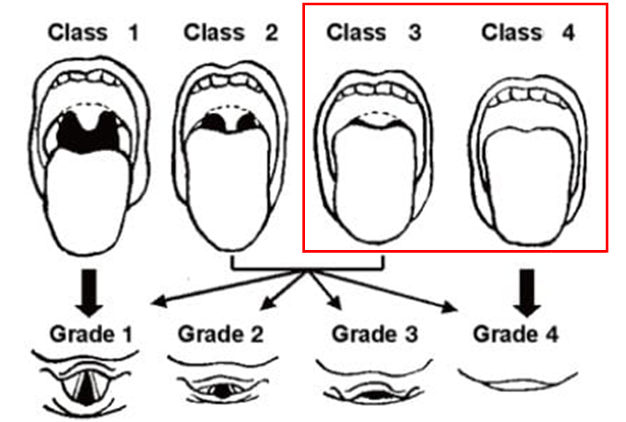
If there are any concerns identified on initial airway assessment above then these MUST be discussed with ED consultant in charge as part of the sedation approval process.



