Eradication of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Children with Cystic Fibrosis
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Disclaimer:
The following guideline has been developed for use within the Royal Hospital for Children, NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde (NHSGGC). The guideline has been developed in collaboration with key stakeholders within NHSGGC, including Microbiology, Cystic Fibrosis, Infectious Disease and Pharmacy teams. The guideline has been approved by the Paediatric Antimicrobial Management Team and ratified by the NHSGGC Antimicrobial Utilisation Committee. The guideline does not account for epidemiology and resistance patterns outside of NHS GGC and use outside of the designated organisation is at the individual’s risk.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is recognized as being a significant respiratory pathogen for patients who have Cystic Fibrosis (CF). Chronic colonisation with Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with poorer clinical outcome and attempted eradication on first culture is aimed at preventing this.1
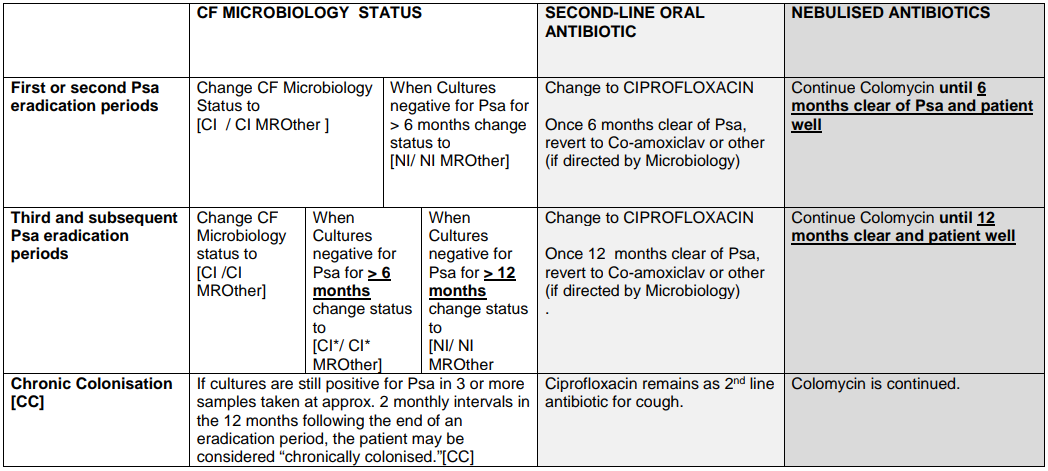
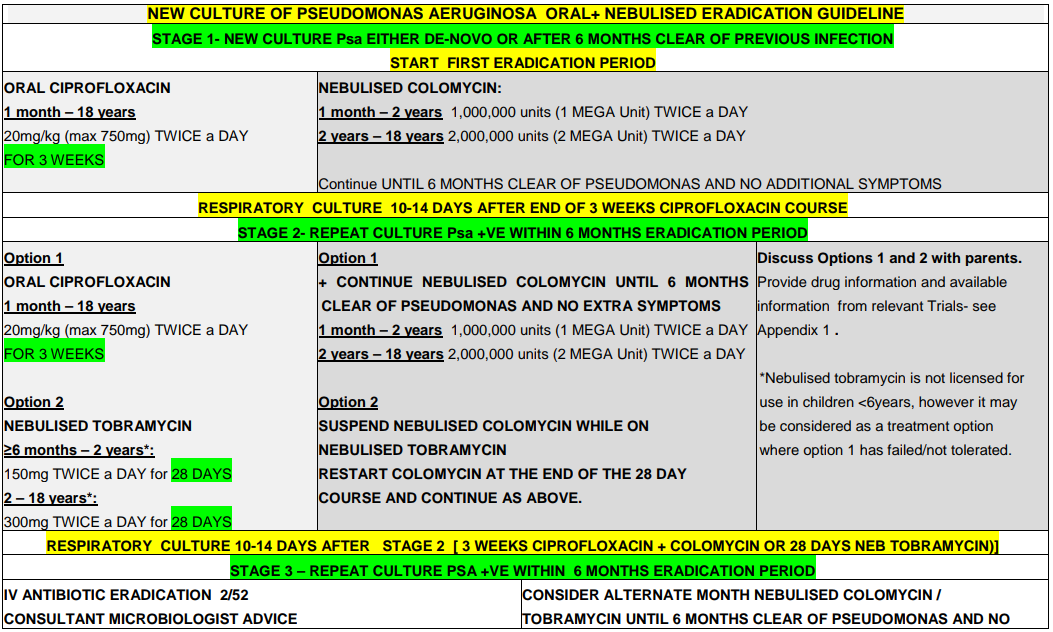
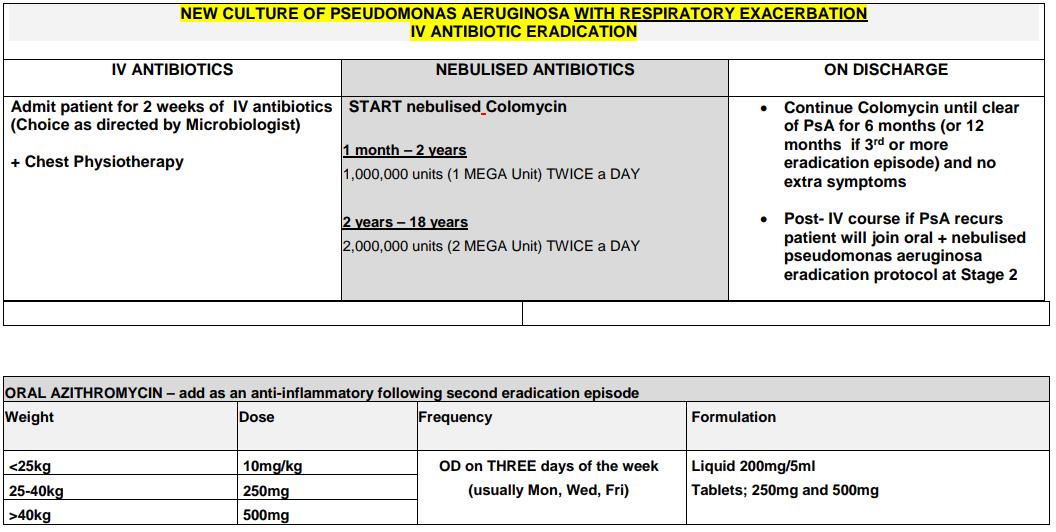
Recommendation: When P. aeruginosa grows from respiratory culture for the first time (or where there is growth in a patient that has been clear of the organism for 6 months or more) eradication should be attempted.2
Please note: if Ps aeruginosa is resistant to Ciprofloxacin please seek Consultant Microbiologist advice.

QtC Prolongation
There is a risk of QtC prolongation in patients commenced on ciprofloxacin. Baseline +/- repeat ECGs are recommended for all children with a cardiac history or where ciprofloxacin is used in combination with other QtC prolonging drugs. Common agents include: domperidone, metoclopramide, azithromycin, ondansetron, azole antifungals. For further information contact Pharmacy.
ANNUAL AUDIT OF:
- NEW AND RECURRENT PSEUDOMONAS RATES
- PSEUDOMONAS SUCCESSFUL ERADICATION RATES
- Compliance with guidance for stopping pseudomonas eradication therapy
- Frederiksen B, Koch C, Hoiby N. Antibiotic treatment of initial colonisation with Pseudomonas aeruginosa postpones chronic infection and prevents deterioration of pulmonary function cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 1997; 23:330- 335.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in people with cystic fibrosis. Suggestions for Prevention and Infection Control. CF Trust 2004 (updated Nov 2016)
- Clinical Guidelines: Care of Children with Cystic Fibrosis 2020; Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospitals, accessed online 03/11/2021 via https://www.rbht.nhs.uk/childrencf
- N. Høiby , B. Frederiksen T. Pressler. Eradication of early Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Department of Clinical Microbiology 9301, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Juliane Maries Vej 22, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark. Danish Cystic Fibrosis Center, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark
- EPIC Study 2012
- Ana C. Blanchard, Eric Horton, Sanja Stanojevic, Louise Taylor, Valerie Waters, Felix Ratjen. Effectiveness of a stepwise Pseudomonas aeruginosa eradication protocol in children with cystic fibrosis. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 16 (2017) 395–400
- BNFC- Drug information, accessed via https://bnfc.nice.org.uk/ 03/11/2021
- Tobramycin (Inhaled) monograph – Paediatric; Children’s Antimicrobial Management Program (ChAMP); Perth Children’s Hospital; Oct
2019
Last reviewed: 22 February 2022
Next review: 22 February 2024
Author(s): Dr Jane Wilkinson
Version: 2
Co-Author(s): Dr Christine Peters, Dr Rosie Hague, Peter Anderson, Jane David, Susan Kafka
Approved By: Antimicrobial Utilisation Committee
Document Id: 702

