Acute Renal Failure Management and Investigation
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Objectives
The following guideline has been developed by clinicians within the Renal Unit at RHC Glasgow.
The objective of this guideline is to aid in the diagnosis, investigation and management or acute renal failure in children. It includes the management of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities in children with acute renal failure.
Scope
This document is intended for use by clinicians in the Management and Investigation of Acute Renal Failure. For further information, contact a clinician within the Renal Unit. Ward office number 0141 452 4563
- Oliguria - Urine Output: - <300ml/m2/day or 0.5ml/kg/hr
- Anuria - Urine Output: - <1ml/kg/day
- Hyperkalaemia - K >6.0 mmol/L on 2 separate occasions
- Clinical Fluid Overload
- Oedema
- Triple rhythm
- Hypertension
Paediatric-Modified RIFLE (pRIFLE) Criteria
| Category | Estimated CCl (eCCL) | Urine Output |
| Risk | eCCl decrease by 25% | <0.5ml/kg/h for 8h |
| Injury | eCCl decrease by 50% | <0.5 ml/kg/h for 16h |
| Failure | eCCl decrease by 75% or eCCL <35 ml/min/1.73 m2 | <0.3 ml/kg/h for 24h or anuric for 12h |
| Loss | Persistent failure >4 weeks | |
| End stage | End-stage renal disease (persistent failure for >3 months) |
| Pre-Renal | Intrinsic Renal | Post-Renal |
|
Hypovolaemia |
Circulatory Insufficiency | Posterior Urethral Valves |
|
Peripheral vasodilatation |
Nephrotoxins | Blocked Catheter |
|
Impaired Cardiac Output |
"Renal Disease" | Neurogenic Bladder |
|
Renal Vessel occlusion |
Myo/haemoglobinuria | Trauma |
|
Nephrotoxic Drugs* |
Tumour infiltrate | Calculi |
|
Hepatorenal Syndrome |
Intratubular obstruction | |
| Increased intraabdominal pressure | Latrogenic Factors |
|
*Avoid giving Ibuprofen
- Patient Weight – Required Daily
- Urine Output
- Blood Pressure
- Hydration Status
- Blood Biochemistry and FBC
- Cardiorespiratory Examination
- Neurological Examination
- Musculoskeletal Examination
- Bruising/Bleeding
- Drug History Investigations
| - U&E’s, LFT’s and CRP | - LDH |
| - Uric acid | - FENa |
| - Magnesium | - Urinalysis |
| - Glucose | - Urinary Sodium, Osmolality |
| - Osmolality | - Microscopy for casts |
| - FBC ± Blood film | - Culture and sensitivity |
| - Coagulation Screen | - Renal Ultrasound |
| - Group and Save |
Consider the following on clinical grounds
| - Parathyroid hormone (if acute on chronic suspected) | - Serum for toxicology/ drug levels |
| - C3 | - Hepatitis Screen |
| - ASO titre, anti DNAse B | - E. Coli Antibody |
| - Antinuclear antibodies/ anti-DNA binding | - Stool culture |
| - Anti-GBM antibodies | - AXR |
| - ANCA (anti neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody) | - MCUG |
| - Blood culture | - Isotope scan |
| - XR left wrist and hand (signs of ROD in acute on chronic) | |
| - Ophthalmology opinion |
| Pre-renal | Intrinsic | Post-renal | ||
| Urine Output | Oliguria | Oliguria - Polyuria | Variable | |
| Uosm (mosm) (newborn) |
>500 (>350) |
<300 (<300) |
<350 (<300)
|
|
| UNa (mmol/L) (newborn) |
<10 |
>40 |
>40 |
|
| FENa (%) (newborn) |
<1 (<2.5) |
>2 (>3) |
<2 (<3)
|
|
| Lab studies | Increased Urea Lower Creatinine |
Hypocalcaemia Hyperphosphataemia Creatinine increases by 45 –130 mmol/L/day |
Hyponatraemia Hyperkalaemia Hyperchloraemic Acidosis |
|
For calculation of FENa- http://www.mdcalc.com/fractional-excretion-of-sodium-fena/
Fluid Management
- Correction of Hypovolaemia
- Fluid Overload (Red Flag):
- Furosemide 2 - 5mg/kg over 1 hour
- Fluid restriction
- Minimalise drug infusion volumes
- Accurate input/output
- Daily weight
- Dialysis
- Beware Polyuria
Aim is to maintain isovolaemia erring on the side of minimal fluid overload.
As a rule of thumb, daily fluid requirements should equal insensible fluid losses plus output (urine, vomiting, drain losses, diarrhoea etc). Insensible fluid losses can be calculated as per the table below:
| Weight | Insensible Fluid Loss |
| 1-10kg |
25ml/kg |
| 10-20kg |
12.5ml/kg |
| >20kg |
5ml/kg |
Electrolyte Abnormalities
Hyponatraemia
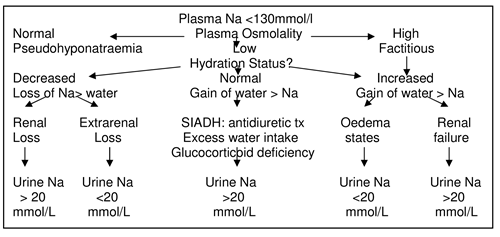
- Salt loss > water loss
- Volume resuscitation
- Sodium deficit (140-Na) x 0.65 x Body weight
- Replace deficit with 0.9% saline, usual maintenance
- Water gain > Na
- Fluid restriction
- Hypertonic saline with loop diuretic
- Mannitol
Hypernatraemia
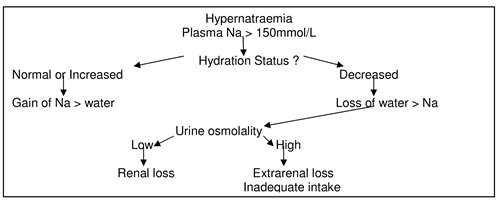
Hypernatraemia may be due to:
- Extrarenal fluid loss in PICU patients
- Excess sodium bicarbonate
- Volume resuscitation
- Water deficit
- weight x 0.65 x ((Actual Na/140)-1))
- Replace with 0.45% saline over 36-72 hrs - Central DI- DDAVP
- Nephrogenic DI- Diuretic therapy
Hypocalcaemia
- Emergency- 0.5ml/kg/hr of 10% Ca Gluconate
- 50ml/kg Ca/kg/day
- If resistant, check Mg
Hyperphosphataemia
- Phosphate restriction
- Phosphate binders e.g. Ca Carbonate
Hypophosphataemia
- Polyuric states
Hyperkalaemia
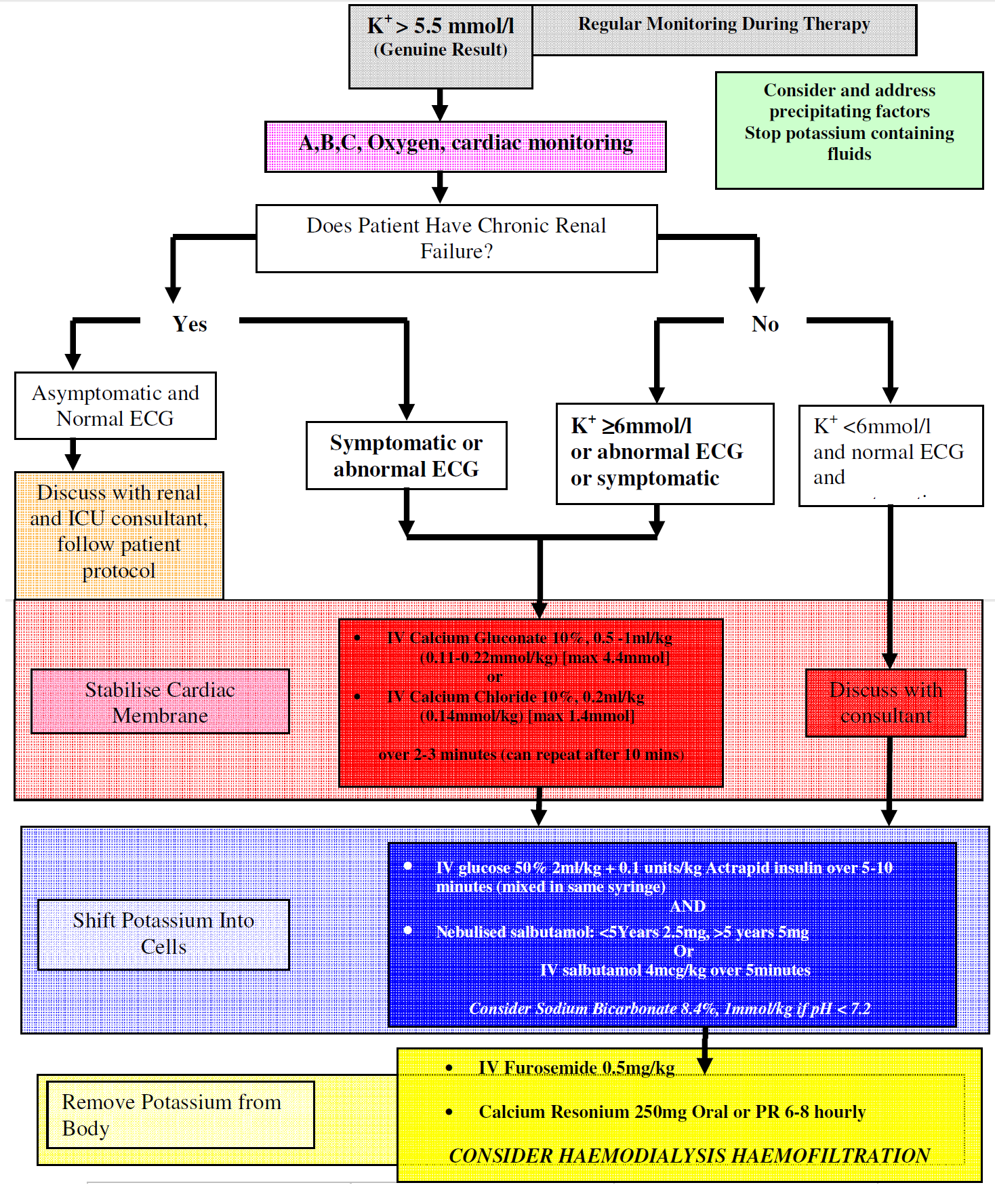
These are invariably acidosis and are often mixed respiratory and metabolic especially in the intensive care setting. Treatment is generally only indicated if there is associated hyperkalaemia or if the acidosis is profound.
Treatment of Acid-Base Disorders
- Base Deficit (mmol) = Base Excess x Weight/3
- Replace half of the deficit initially
- Sodium Bicarbonate is hypertonic with a risk of CNS complications or hypernatraemia and is only effective with adequate ventilation.
- Rapid correction of acidosis may cause hypocalcaemia and tetany or seizures
- Therefore rapid correction to be avoided
Acute renal failure is a hypercatabolic state and requires aggressive nutritional support. Unlike adults there is no indication for dietary protein restriction, which should be delivered in amino acids or protein of high biological value. The majority of calories should however be delivered as carbohydrates.
- Calories 1400 kcal/m2/day
- Protein 0.6g/kg/day (1.5g if dialysed)
- Intralipid - medium chain triglycerides
- Folate and Vitamin supplementation
May relate solely to salt and water overload and therefore in the presence of oligo/anuria and in the absence of hypovolaemia an initial trial of diuretic therapy is justified.
For further details of the management and investigation of hypertension – see appropriate protocol.
Drug therapy for the emergency treatment of hypertension is outlined below.
| Agent | Dose | Onset | Action | Complications |
| Labetalol | 1-5 mg/kg/hr | 3-5 min | Alpha & beta Blocker | Hypoglycaemia Well tolerated |
| Nifedipine | 0.25-0.5 mg/kg | sublingual | 5-10 min Ca channel blocker |
Headache, |
| Sodium Nitroprusside | 0.5-8 ug/kg/min as IV infusion | Instant | Direct vasodilator | Thiocyanate poisoning |
| Clonidine | 2-6 ug/kg | ~10 min | Central alpha 2 Agonist | Depression Rebound |
| Hydralazine | 0.2 to 15mg/dose IV bolus 4-6ug/kg/min IVI |
5-10 min | Direct vasodilator | Headache, vomiting, tachycardia |
| Frusemide |
1-3mg/kg over 15min |
Diuretic |
Volume depletion, |
Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. Acute kidney injury app.
Last reviewed: 25 November 2020
Next review: 31 December 2023
Author(s): Ian Ramage
Approved By: Clinical Effectiveness

