Bomb blast injuries in children: antibiotic management
This guidance is adapted from Public Health England guidance (issued May 2017) and is intended as initial empirical prophylaxis. The advice contained within this guidance is suitable for ALL age groups of patients. Further advice on ongoing antibiotic management may be provided by microbiology/infectious diseases teams if required. In addition to antibiotics, tetanus and blood-borne virus exposure should be considered.
It is important to recognize that important characteristics of such events may include:
- Blast injuries involving embedded metalwork (e.g. nuts, bolts)
- Large numbers of victims may originate from outside of the incident area
Tetanus immunisation
ALL bomb blast victims with injuries must have their tetanus immunisation status checked and treated according to the extant advice on management of patients with tetanus prone wounds in the ‘Green Book’ Tetanus: the Green Book, chapter 30 - GOV.UK (www.gov.uk)
Hepatitis B vaccination
ALL patients who sustained injuries that breached the skin must have their immunisation status checked and treated according to the extant advice on Hepatitis B prophylaxis in the ‘Green book’ Hepatitis B: the Green Book, chapter 18 – GOV.UK (www.gov.uk).
Patients who are discharged from inpatient care before completion of an accelerated hepatitis B vaccination course should receive the remaining doses of vaccine either at out-patient follow up, or by arrangement with the relevant immunisation provider.
ALL patients should be tested at 3 months to determine their hepatitis B vaccine response and at 3 months and 6 months to determine their hepatitis C and HIV status.
Post exposure prophylaxis for HIV
HIV PEP is not usually required.
Discuss with the Infectious Disease Consultant on-call if uncertain (via RHC switchboard).
|
Injury |
Antibiotic prophylaxis (see appendix 1 for doses) |
|
Soft tissue injury
(NO foreign body in situ) |
IV co amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: IV Clindamycin and gentamicin Continue IV treatment until first surgical debridement/washout Then switch to PO Co-amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: PO Clindamycin and Ciprofloxacin Duration: 5 days (minimum) |
|
Soft tissue injury (Foreign body in situ) |
IV Co amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: IV Clindamycin and Gentamicin Continue IV treatment until first surgical debridement/washout and removal of foreign body Then switch to PO Co-amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: PO Clindamycin and Ciprofloxacin Duration: 7 days (minimum – consider up to 14 days) Seek advice from microbiology/Infectious Disease teams re duration if foreign body remains in situ. |
|
Open Fractures Or ‘Through and through’ fractures Or Intra-articular injuries |
IV Co-amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: IV Clindamycin and Gentamicin Continue IV antibiotics until soft tissue closure OR for a maximum of 72 hours. Prolonged oral therapy may be required after this, please seek advice from the microbiology/Infectious Diseases teams. |
|
Penetrating CNS injury |
IV Ceftriaxone (high dose) PLUS IV Metronidazole IVOS to PO metronidazole when able to swallow, absorb and clinically stable/showing signs of improvement. Duration: |
|
Open skull fracture from penetrating trauma |
IV Ceftriaxone (high dose) until closure then discuss duration of IV therapy and oral switch with microbiology/Infectious Disease teams. |
|
CSF leak post skull fracture |
No antibiotics required Give Pneumovax |
|
Penetrating eye injury |
PO/IV Ciprofloxacin AND PO/IV Clindamycin (use IV route if oral route compromised) AND Topical Chloramphenicol, 0.5% drops every 2 hours and 1% eye ointment at night Assess daily for PO route. Duration: 2 weeks if foreign body removed Seek advice from microbiology/Infectious Disease teams re duration if foreign body remains in situ. |
|
Internal ear injury |
Keep clean and dry. Urgent referral to ENT for examination and removal of debris/clots and instillation of antibiotic ear drops if required. |
|
Penetrating abdominal injury or chest trauma |
IV Co-amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: Clindamycin and Gentamicin Add IV Fluconazole if any spillage of gastrointestinal contents or perforation (review regularly with microbiology/Infectious Diseases teams) Review daily for IVOS - Switch to PO Co-amoxiclav Penicillin allergy: Clindamycin and Ciprofloxacin Duration: Minimum 7 days following surgery Seek advice from microbiology/Infectious Disease teams re duration if foreign body remains in situ |
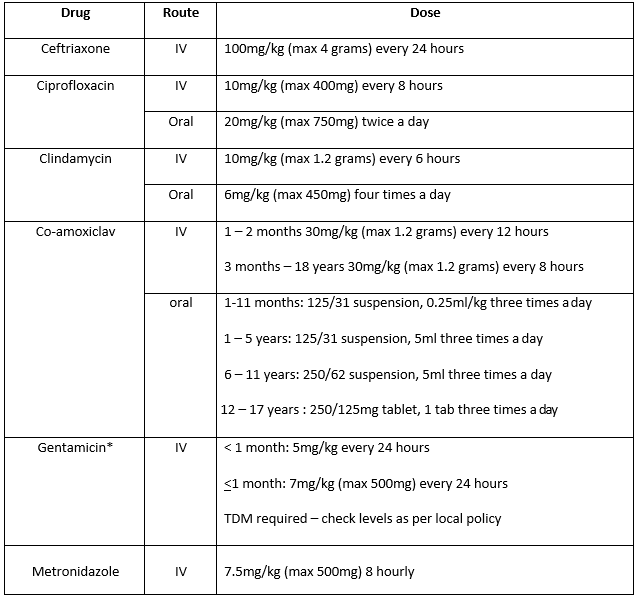
*Note – Caution should be taken when dosing gentamicin in patients who are overweight/obese. Dose on ideal body weight. Dose adjust if renal impairment. Contact Pharmacy for advice.
Public Health England. Antibiotic Prophylaxis Guidance for Bomb Blast Victims. V 1.0, 2017.
UK Health Security Agency. Hepatitis B: The Green Book, Chapter 18, Updated February 2022.
UK Health Security Agency. Tetanus: The Green Book, Chapter 30, Updated June 2022.
Last reviewed: 13 August 2024
Next review: 30 November 2026
Author(s): Susan Kafka
Version: 3
Approved By: Antimicrobial Utilisation Committee

