Epistaxis management in children
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Objectives
Guidance for the assessment and management of children presenting with epistaxis.
Scope
A guideline is intended to assist healthcare professionals in the choice of disease-specific treatments.
Clinical judgement should be exercised on the applicability of any guideline, influenced by individual patient characteristics. Clinicians should be mindful of the potential for harmful polypharmacy and increased susceptibility to adverse drug reactions in patients with multiple morbidities or frailty.
If, after discussion with the patient or carer, there are good reasons for not following a guideline, it is good practice to record these and communicate them to others involved in the care of the patient.
Audience
Emergency department medical and nursing staff.
November 2023: This guidance is currently under review as it has gone beyond the standard review date. It reflects best practice at the time of authorship / last review and remains safe for use. If there are any concerns regarding the content then please consult with senior clinical staff to confirm.
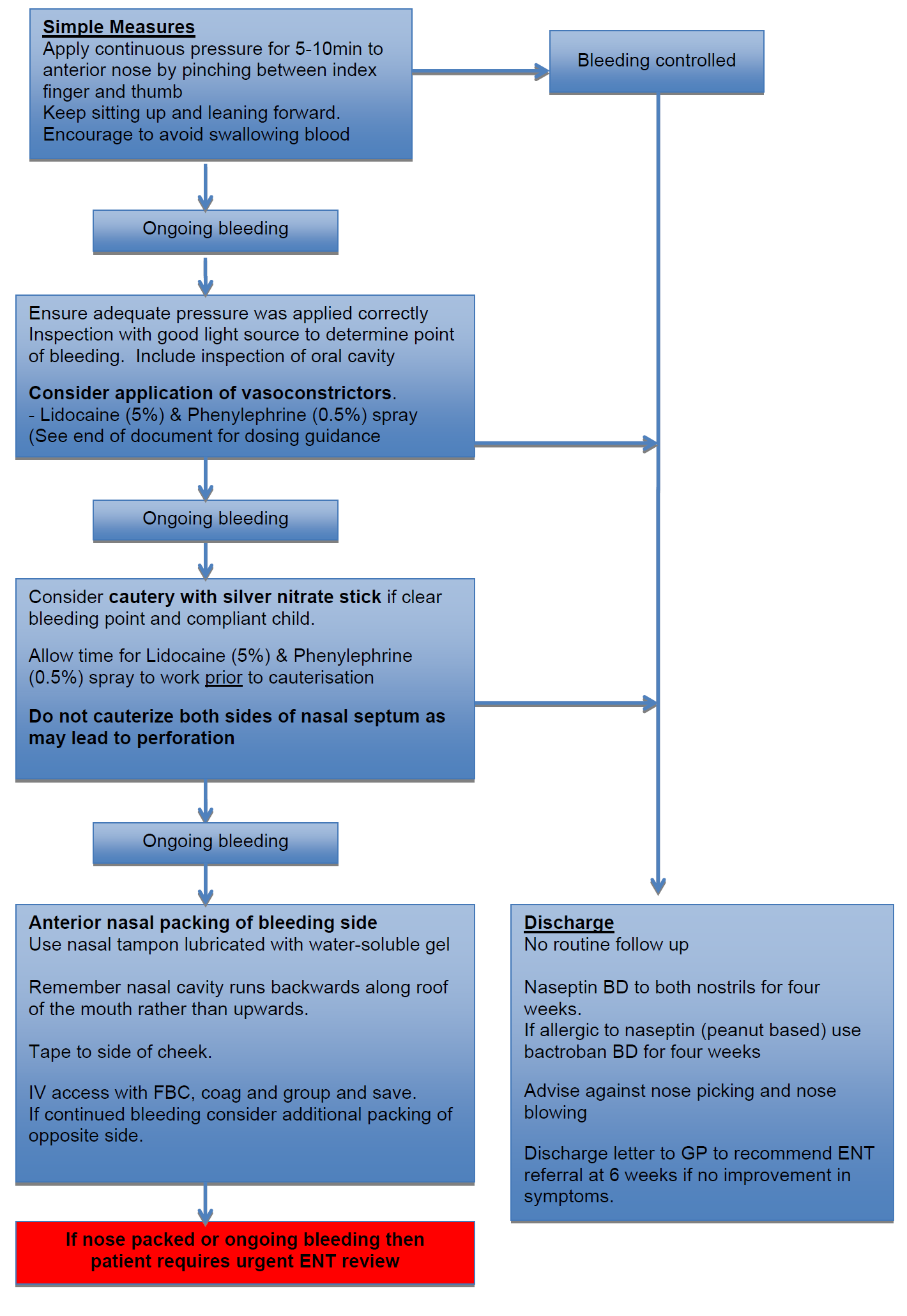
Epistaxis is a common childhood complaint and is normally benign and self-limiting. Epistaxis in children is most commonly caused by minor trauma such as nose picking. Alternative diagnosis to consider include recent URTI, allergic rhinitis, nasal foreign body and more rarely bleeding disorders. Epistaxis is unusual in children under the age of two and alternative diagnosis should be considered. Most bleeding occurs anteriorly from Little’s area.
History:
- Length of bleeding (if > 30 mins despite appropriate 1st aid then consider coagulopathy)
- Side of bleeding
- Periodicity of episodes (how many weeks/ months)
- Frequency of episodes
- Associated nasal discharge (if unilateral consider foreign body)
- History of nasal trauma (old or new)
- Bleeding from other sites Past history of easy bruising/ bleeding problems/ haematological abnormality/malignancy
- Family history of bleeding disorders
- Medications e.g. warfarin, nasal corticosteroids.
Age
Estimated or actual Weight (kg)
Maximum number of sprays
1
10
1
2
12
1
3
14
2
4
16
2
5
18
2
6
25
3
7
28
4
8
31
4
9
34
5
10
37
5
11
40
6
12+
43+
Max 8
Age
Formula
0-12 months
Weight (in kg) = (0.5 x age in months) + 4
1-5 years
Weight (in kg) = (2 x age in years) + 8
6-12 years
Weight (in kg) = (3 x age in years) + 7
Instructions for use:
Prime spray nozzle after attachment by spraying 3 times before administering to patient.
For Epistaxis:
Can be sprayed onto a cotton wool ball and applied up nostril or sprayed directly to point of bleeding.
For Tonsillar bleeding:
Spray directly on to the point of bleeding.
Last reviewed: 16 September 2019
Next review: 31 October 2024
Author(s): Shona Leighton
Co-Author(s): Corresponding author: Steven Foster
Approved By: Clinical Effectiveness